Human skulls at the Nyamata Genocide Memorial
Human skulls at the Nyamata Genocide Memorial
There are many ways to decrease human numbers, and most of them should be shunned. Indeed, some of them are quite horrifying. In this and subsequent columns I’ll write about some of them.
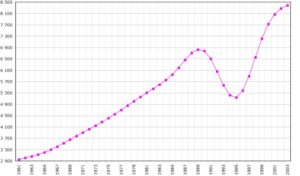
It has been more than 20 years since the Rwandan genocide, but it stands out in my mind as the worst episode of human slaughter in recent history. Estimates of the number of people killed in a terrible 100 day period range from 1/2 million to a million. The population of Rwanda at that time was less than 8 million; a huge proportion of this small country’s people killed each other. In addition, an estimated 2 million were displaced or fled the country.
Genocide is the intentional destruction of a national, ethnic, racial, or religious group. Theories about the causes of genocide include tribalism, autocratic rulers and lack of resources. An article about this genocide, “Remember Rwanda†by James Gasana was published in WorldWatch. Gasana is Rwandan and had held 2 different cabinet positions in that country. In this article he noted that murder was most common where people went to bed hungry. That hunger, contributed to by overpopulation, apparently was part of what fueled the killing
In 1994 Rwanda had an almost entirely agricultural economy and was overpopulated. As the population rose the size of landholdings shrank and the overworked land became less productive. Even if people wanted to limit their fertility, the predominant religion, Roman Catholicism, preached against “artificial†contraception.
That is in the past. With international help and amazing resilience, the Rwandan people have put that terrible part of their history behind them. However, another country appears to be enduring a religiously motivated genocide. The Rohingya people in Myanmar (Burma) are both an ethnic minority and, as Muslims, have different religious beliefs from the Buddhist majority.
Genocide Watch lists 10 stages that are seen in preparation for and carrying out a genocide: Classification, Symbolization, Discrimination, Dehumanization, Organization, Polarization, Preparation, Persecution, Extermination and Denial. Most of these stages can be seen with the treatment of the Rohingyas.
Although they live in Myanmar, the Rohingyas aren’t allowed citizenship—classification. While they are not forced to wear identifying symbols, their freedom is restricted in other ways. They must live in ghettoes and are restricted by curfews—organization and polarization. Mobs attack Rohingya settlements while officials offer no protection—preparation. “Security†forces have killed thousands of Rohingyas while others have been tortured, “disappeared†or have suffered rape—extermination. The country admits to no wrongdoing—denial.
Perhaps the most dire of the measures against the Rohingyas is limitation of their reproductive rights. While there is no limitation on other people in Myanmar, the Rohingyas are only allowed to have two children. Apparently the Muslims tend to have larger families than the Buddhists in the same area. The state officials’ reason for this limitation is to “…ease tensions between Buddhists and their Muslim Rohingya neighbors.†Even if this is the true motivation, legislating the number of children in a family is wrong.
Unfortunately, Myanmar and Rwanda are not unique; there are many historical examples of peoples being singled out and exterminated. In the chapter on genocide, “The Great Big Book of Horrible Things†tallies an estimated 32 million deaths from genocides in the past 3 millennia. This includes a huge but unknown number of indigenous people killed in the Americas when we Europeans invaded.
Currently there are several countries where genocide is happening or is very likely. These include South Sudan, Sudan, Syria, Yemen and the Democratic Republic of Congo, all of which have unstable governments and terrible records of civil rights.
What can we do to prevent genocide? In “Warning Signs of Genocide: an anthropological perspective†Drs. Gene and Barbara Anderson state that the most important protection against genocide is critical thinking—the process of independently analyzing, synthesizing, and evaluating information as a guide to behavior and beliefs. They have written a second book, “Halting Genocide in Americaâ€, in which they are concerned that some people in the USA are already taking steps along the road to genocide.
Genocide is perhaps the most vicious way to slow population growth, but there are several others on my list of means to reject. Nature tends to limit populations with disease and famine, over which we have only limited control. Some other ways of slowing growth are imposed by people and governments. These include eugenics, family size coercion, war, gun violence, and the Voluntary Extinction Movement. More about them in future essays.
© Richard Grossman MD, 2018
Graph showing dip in Rwandan population after genocide, followed by recovery.